80% vs 90%+ Furnaces: What Efficiency Really Means for Your Home
If you’ve ever stood in front of your furnace and wondered why there are different efficiency ratings, you’re not alone. Most homeowners hear “80%” or “90%+” and assume it’s just a number on a sticker. In reality, that number has a lot to do with how your furnace is built, how much heat you actually get, and how much money stays in your pocket every winter.
Let’s break it down in plain English, neighbor to neighbor.
The Two Main Furnace Efficiencies You’ll See
When you’re shopping for a gas furnace, almost everything falls into two categories:
-
80% efficiency furnaces
-
90% or higher efficiency furnaces (often 95–98%)
That efficiency rating is called AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency). It tells you how much of the fuel you pay for actually becomes heat in your home.
An 80% furnace turns about 80% of the gas it burns into usable heat. The other 20% goes right out the vent.
A 90%+ furnace keeps much more of that heat inside your house where it belongs.
The Real Difference Is the Heat Exchanger
Here’s the key thing most sales brochures gloss over:
The efficiency difference is almost entirely determined by the heat exchanger.
In heating and air conditioning, the easiest way to make equipment more efficient is simple—you add more metal.
That’s exactly what manufacturers did.
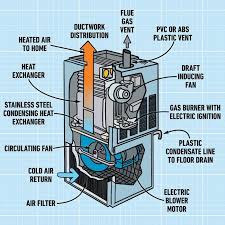
How an 80% Furnace Works
An 80% furnace has one primary heat exchanger.
-
Gas burns in the combustion chamber.
-
Heat transfers through the metal heat exchanger.
-
Warm air is blown into your home.
-
Hot exhaust gases are vented out through a metal flue, usually up through the roof.
Those exhaust gases are still pretty warm. That’s where the “lost” 20% goes.
How a 90%+ Furnace Is Different
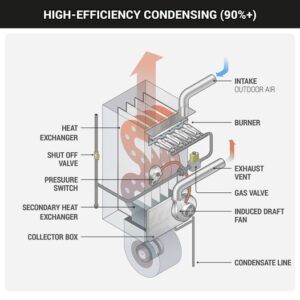
A 90%+ furnace does everything an 80% furnace does plus one more step.
It adds a secondary heat exchanger.
After the primary heat exchanger pulls out most of the heat, the exhaust gases go through a second metal heat exchanger that squeezes out even more warmth. By the time those gases leave the system, they’re cool enough to vent through PVC pipe out the side of your house.
That extra metal is what boosts efficiency.
Why Higher Efficiency Matters to Homeowners
Efficiency isn’t just a technical detail. It affects your comfort, your bills, and even how your home feels in winter.
Lower Monthly Heating Bills
This one’s straightforward.
If you’re paying for gas anyway, wouldn’t you rather keep more of that heat?
A 95% furnace wastes far less energy than an 80% furnace. Over a Utah winter—especially during long cold stretches in places like Salt Lake City, Draper, or Heber—that difference adds up fast.
More Consistent, Comfortable Heat
High-efficiency furnaces tend to run longer, gentler heating cycles. That means:
-
Fewer hot-and-cold swings
-
More even temperatures from room to room
-
Less of that “blast of hot air, then nothing” feeling
Homeowners often tell us their house just feels steadier after upgrading.
Better for Indoor Air and Venting
Because 90%+ furnaces use sealed combustion and PVC venting, they:
-
Pull air from outside instead of your home
-
Reduce drafts and backdraft risks
-
Improve overall indoor air quality
This matters a lot in winter inversion season along the Wasatch Front, when every bit of indoor air quality counts.
Smarter Long-Term Investment
An 80% furnace usually costs less upfront, but it costs more to run year after year. A high-efficiency furnace costs a bit more initially, but:
-
Saves money over its lifespan
-
Often qualifies for rebates or energy incentives
-
Adds value when selling your home
For many homeowners, the math works in their favor sooner than they expect.
Why 80% Furnaces Still Exist
You might wonder why anyone would still choose an 80% furnace.
In some older homes, venting configurations or budget constraints make them the easier short-term option. They’re also mechanically simpler, which can appeal to certain homeowners.
That said, in most Utah homes today, a 90%+ furnace is the better long-term solution if installation allows for it.
Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Home
The “best” furnace isn’t just about efficiency—it’s about how your home is built, how it’s vented, and how long you plan to stay there. That’s why a proper evaluation matters more than a quick quote.
If you’re weighing options or replacing an aging system, having a local expert look at your setup can save you from costly surprises later.
Need service? Call (801) 876-5222 or schedule an appointment online.
References
-
U.S. Department of Energy – Furnace Efficiency and AFUE
https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/furnaces-and-boilers - At Your Service Pros
- ENERGY STAR – Tax credit High Efficiency

